Ankle arthrosis is a dystrophic degenerative pathological disease characterized by the gradual destruction of cartilage, joints and adjacent bone structures, as well as ligaments and even muscles, leading to impaired mobility and even disability. The reason for the development of such a pathology may be traumatic injury, which develops post-traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint, metabolic disorders in the body or some inflammatory diseases.
Do not self-medicate. At the first sign of illness, consult a doctor.
The diagnosis of pathology is determined based on the patient's complaints, as well as the results of X-ray and ultrasound examinations. The disease should be treated conservatively, and surgery is indicated only in severe (negligent) cases.
The disease has a chronic wavy course, periods of exacerbation are replaced by periods of calm, but still the development of pathology continues, even in the absence of symptoms, so if treated, over time, the ankle is completely destroyed. not implemented. Older people often suffer from osteoarthritis due to natural metabolic processes in the body, but there are other reasons for the development of osteoarthritis.
Reasons
In medical practice, there are two types of osteoarthritis: primary and secondary. Primary develops as an independent pathology for no apparent reason. The second is the result of any adverse effects, such as traumatic injuries.
The main reasons for the onset of the disease may be:
- diabetes;
- thyroid disease;
- excess weight;
- persistent microtrauma that can occur in people who exercise or regularly walk on high heels;
- rheumatic pathologies;
- traumatic injuries in this area (fracture, dislocation);
- inflammatory processes that develop as a result of diseases such as gout, arthritis;
- hereditary metabolic disorders that cause thinning of tissues.
Sometimes the disease occurs in children and its causes can be:
- tissue dysplasia;
- congenital anomalies;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- trauma;
- articular inflammatory diseases.
Degrees and symptoms
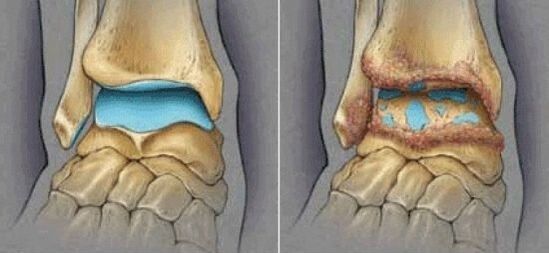
There are of course three degrees that determine the symptoms of ankle osteoarthritis. It is important to remember that the disease progresses gradually, so the disorders in the joint will be insignificant at first, and then become more pronounced. At the same time, the resulting changes are no longer irreversible, and at one stage or another the treatment of pathology will consist only in preventing the development of the disease.
In the first stage of the disease, the tissue becomes thinner, and this does not happen on the entire surface, but in individual parts - special islets.
Primary disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- extreme fatigue with long-term stress on the legs;
- discomfort in the joint area after walking on heels;
- minor pain that disappears at rest.
X-ray or ultrasound examination does not reveal any pathological changes in the joint, so doctors can not diagnose at this stage.
In the early stages of the disease can be treated at home with folk remedies - first of all, refrain from wearing high-heeled shoes, lose weight (if necessary), do exercise therapy, as well as use some folk methods. are discussed below.
With the second stage of the pathological process, it falls on the bone under load in the areas where the tissue is thinned. For this reason, it grows to form osteophytes that damage healthy areas of cartilage tissue in or near or near it. The symptoms of second-degree osteoarthritis are more pronounced:
- pain with less stress, does not pass immediately after stopping;
- occurrence of night pains that interfere with sleep quality;
- limited joint mobility in the morning (needs some time to work);
- joint reaction to weather conditions.
In the third degree, deforming arthrosis of the ankle develops. During this period, all the tissues of the joint become as thin as bone structures, the muscles are overstretched on the one hand, and cramped on the other, trying to keep the joint in the correct position. Symptoms of the third degree of a pathology, such as deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint, are associated with complete impairment of its mobility and severe pain:
- severe pain that does not stop even at rest;
- requires such long-term development to make minimal joint movements in the morning;
- feeling of wheezing;
- the need to take painkillers to relieve pain;
- restriction or even complete disruption of mobility in the affected area.
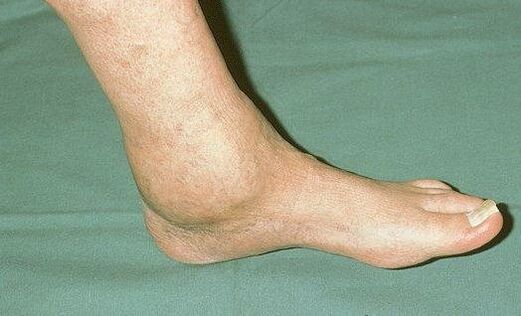
Pathology such as traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint is characterized by some other symptoms:
- swelling and redness in the affected area;
- increase in local temperature;
- crunch or crepitus.
Diagnosis and treatment
X-ray examination plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of the disease. However, it is important that the physician listens to the patient's complaints, which may allow the diagnosis to be made at an early stage when no radiographic changes are seen. In severe cases, the patient is referred for CT or MRI of the ankle.
Treatment of ankle arthrosis depends on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage, it is enough to change your lifestyle and proper motor regime. At this stage, massage and exercise therapy will be useful to improve blood circulation. If we talk about treatment with folk remedies that can be used at home, then it can reduce pain and relieve the inflammatory process. This folk remedy that everyone can use at home:
- apply olive oil on the affected area in the morning;
- use of burdock leaves in the form of supplements for painful joints for the whole night;
- prepare comfrey ointment and rub it on the affected area twice a day;
- take the mummy in tablet form and rub it on the affected joint.
There are other alternative methods of treatment, but it should be remembered that they are not a panacea for the disease, and only their combined use of medication, diet, exercise therapy and proper lifestyle will stop the process of destruction.
If we talk about the drug treatment of osteoarthritis of the ankle, it involves the use of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs. In addition, patients are prescribed chondroprotectors that protect the joint for a long time (at least six months).
The use of intravenous drugs such as niacin is indicated to improve the nutrition of the affected compound. Treatment with hyaluronic acid is considered effective and in some cases requires a single application of hormones.
The disease should be treated with physiotherapy. In each case, special exercises are performed for arthrosis of the ankle joint, selected by a physiotherapist. It is very important that gymnastics does not cause pain to the patient with arthrosis of the ankle joint, but at the same time the person should feel a little discomfort, because otherwise the procedure will be ineffective.
Other physiotherapeutic methods include:
- magnetotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- thermal procedures and some other types of exposure.
Surgery for this disease is indicated only in severe cases when the joint is completely destroyed. Often patients have joint prostheses, which return the limbs to mobility, but other surgical methods are also used - the doctor makes a choice based on the patient's condition.

























